As the physical properties of single crystal and polycrystalline diamond are different, the applications of these two different abrasives are then naturally different. For example, in the field of semiconductor, when tough materials as sapphire and silicon carbide are needed to be smoothly polished without damage, the use of polycrystalline diamond polishing liquid is more suitable than single crystal diamond. Why is this?
Single Crystal Features VS Polycrystalline Diamond Features:
Single Crystal Features
Uniform Atomic Structure: Single crystals possess a continuous and unbroken lattice structure throughout the material, ensuring consistent properties in all directions within the crystal.
High Purity: Single crystals are often free from grain boundaries or imperfections, which leads to fewer defects and higher purity compared to polycrystalline materials.
Anisotropy: Due to their uniform atomic arrangement, single crystals exhibit anisotropic properties, meaning their mechanical, optical, and electrical behaviors vary depending on the direction within the crystal.
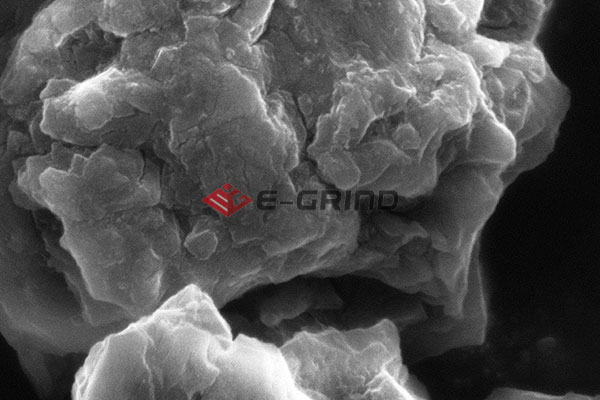

Key Properities of Polycrystalline Diamond
Exceptional hardness and wear resistance: The unmatched hardness of 10,000 HV in nature makes this material highly durable, with wear resistance nearly 100 times greater than that of carbide inserts.
Anisotropic single-crystal diamond properties: The hardness, wear resistance, microstructural strength, and processing difficulty of single-crystal diamond vary significantly based on the crystal surface and orientation. Therefore, when designing and manufacturing monocrystalline diamond tools, it's crucial to select the proper crystal direction. Properly choosing the orientation of the tool's front and back faces is key in creating efficient single-crystal diamond tools.
Low friction coefficient: As a commnon
synthetic diamond powder, PCD inserts have a significantly lower friction coefficient when machining certain non-ferrous materials, roughly half that of carbide inserts, typically around 0.2.
Extremely sharp cutting edge: PCD cutting edges feature a radius of 0.1 to 0.5 µm, while natural single-crystal diamond tools can achieve even finer radii, ranging from 0.002 to 0.005 µm. As a result, natural diamond tools enable ultra-thin and ultra-precise machining.

The Difference Between Single Crystal and Polycrystalline Diamond:
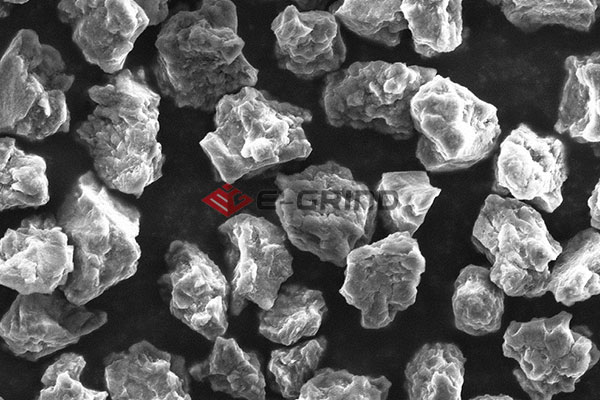
The main difference between single crystal and polycrystalline diamond lies in the structure of diamond particles, which can actually be clearly seen under the microscope. Although both abrasives are irregular polyhedral block particles, the polycrystalline diamond grains are arranged in disorder. As a result, it holds good toughness, and can withstand higher stress.
Why Use Polycrystalline Diamond?
Meanwhile, since the polycrystalline diamond also has the characteristics of large surface area and cleavability, the self-sharpening properties of polycrystalline diamond are also very good. During the grinding and polishing process, as the crystallite particles fall off, the polycrystalline diamond abrasive will continuously expose more of the same rough and sharp crystallites. This means that regardless of the direction of the workpiece, the polycrystalline diamond has a lot of cutting edges. As a consequence, not only can the processing steps of raw materials be effectively reduced, but the production efficiency can also be improved.